


#Molar entropy series
If a mole of a solid substance is a perfectly ordered solid at 0 K, then if the solid warmed by its surroundings to 298.15 K without melting, its absolute molar entropy would be the sum of a series of N stepwise and reversible entropy changes. However, the residual entropy is often quite negligible and can be accounted for when it occurs using statistical mechanics. ) These contributions to the entropy are always present, because crystals always grow at a finite rate and at temperature. Thus, molar entropy of H 2O(s) < H 2 O ( s) < molar entropy of H 2O(l) H 2 O ( l). In ice, molecules of H 2O H 2 O are less random than in liquid water. This can be due to crystallographic defects, dislocations, and/or incomplete rotational quenching within the solid, as originally pointed out by Linus Pauling. The standard molar entropy of H 2O(l) H 2 O ( l) is 70J K 1mol 1 70 J K - 1 m o l - 1. However, this assumes that the material forms a ' perfect crystal' without any residual entropy. The entropy of a pure crystalline structure can be 0 J⋅mol −1⋅K −1 only at 0 K, according to the third law of thermodynamics.

That is, an element in its standard state has a definite, nonzero value of S at room temperature. Unlike standard enthalpies of formation, the value of S° is absolute. Is usually given the symbol S°, and has units of joules per mole kelvin (J⋅mol −1⋅K −1). These are often (but not necessarily) chosen to be the standard temperature and pressure. In chemistry, the standard molar entropy is the entropy content of one mole of substance, under standard conditions (NOT STP). Calculate the enthalpy and entropy of fusion of the solid. Hydrogen bond basicity of ionic liquids and molar entropy of hydration of salts as major descriptors in the formation of aqueous biphasic systems Helena. At 1.2 MPa the melting temperature changes to 429.26 K. The molar volume of the liquid at this temperature and pressure is 152.6 cm3/mol.
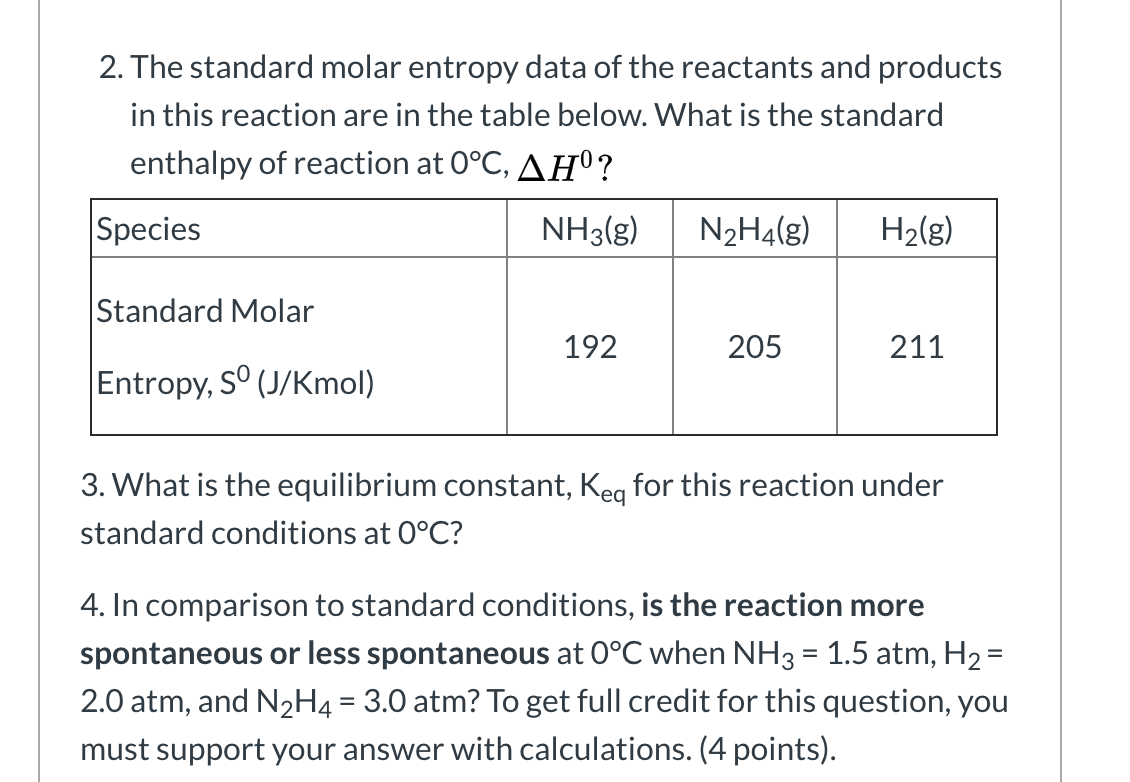
however my texbook answer key says that the answer is 380 J K 1 m o l 1. The entropy is an extensive property dependent on the variables of state P, T, n1, n2., where n i is the number of moles of i, and the molar entropy is. Entropy is a measure of disorder, so compounds with higher molar entropy. Assume the change is reversible and the temperature remains constant.In chemistry, the standard molar entropy is the entropy content of one mole of pure substance at a standard state of pressure and any temperature of interest. The molar volume of a certain solid is 142.0 cm3/mol at 1.00 atm and 427.15 K, its melting temperature. If a substance has a molar heat of vaporization of 3.05 × 10 4 J / m o l and a normal boiling temperature of 80.0 C, what is the value of its molar entropy of vaporization S v a p in J K 1 m o l 1 I got. The molar entropy is defined as the amount of entropy in one mole of a substance. The standard molar entropy of H 2O(l) H 2 O ( l) is 70J K 1mol 1 70 J K - 1 m o l - 1. Determine the change in entropy (in J/K) of water when 425 kJ of heat is applied to it at 50 oC. answered Sep 28 by UrmillaSahu (58.8k points) selected Sep 28 by NiharBasu.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
